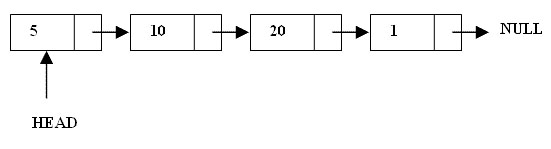
Singly-linked list is a list of elements in which the elements of the list can be placed anywhere in heap memory. All of list elements are linked together with each other using an explicit link field, that is, by storing the address of the next element in the link field of the previous element. Singly-linked list has a dynamic size and its size can be determined at run-time not compile time. Here the picture which demonstrate a singly-linked list. Their are four elements in the list. The head pointer is the pointer pointing to the first element of the list.
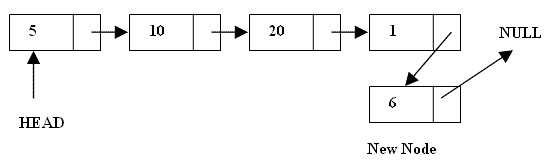
Add a New Element to a Singly-linked List
This picture demonstrates how to add a new elemen to the list. The process is simple as follows:
- If the existing list is empty we need to insert a new element (or node) as the starting node
- Otherwise we traverses the existing list to get the pointer to the last node of it;
Create a new node.
Change the next pointer of the last node to the new node.
The next pointer of new node is pointed to NULL and it becomes the last node of the list.
Implement Singly-linked List in C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node{
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node* add(struct node *head, int data){
struct node *tmp;
if(head == NULL){
head=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(head == NULL){
printf("Error! memory is not available\n");
exit(0);
}
head-> data = data;
head-> next = head;
}else{
tmp = head;
while (tmp-> next != head)
tmp = tmp-> next;
tmp-> next = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if(tmp -> next == NULL)
{
printf("Error! memory is not available\n");
exit(0);
}
tmp = tmp-> next;
tmp-> data = data;
tmp-> next = head;
}
return head;
}
void printlist(struct node *head)
{
struct node *current;
current = head;
if(current!= NULL)
{
do
{
printf("%d\t",current->data);
current = current->next;
} while (current!= head);
printf("\n");
}
else
printf("The list is empty\n");
}
void destroy(struct node *head)
{
struct node *current, *tmp;
current = head->next;
head->next = NULL;
while(current != NULL) {
tmp = current->next;
free(current);
current = tmp;
}
}
void main()
{
struct node *head = NULL;
head = add(head,1); /* 1 */
printlist(head);
head = add(head,20);/* 20 */
printlist(head);
head = add(head,10);/* 1 20 10 */
printlist(head);
head = add(head,5); /* 1 20 10 5*/
printlist(head);
destroy(head);
getchar();
}