Quantization, coding, and prediction
Choosing the bits: quantization and coding
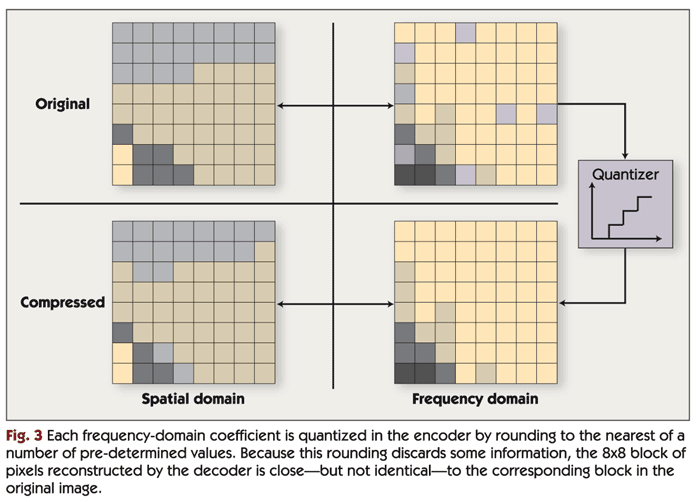
After the block transform is performed, the transform coefficients for each block are compressed using quantization and coding. Quantization reduces the precision of the transform coefficients in a biased manner: more bits are used for low-frequency coefficients and fewer bits for high-frequency coefficients. This takes advantage of the fact, as noted above, that human vision is more sensitive to low-frequency information, so the high-frequency information can be more approximate. Many bits are discarded in this step. For example, a 12-bit coefficient may be rounded to the nearest of 32 predetermined values. Each of these 32 values can be represented with a five-bit symbol. In the decompression algorithm, the coefficients are "dequantized"; i.e., the five-bit symbol is converted back to the 12-bit predetermined value used in the encoder. As illustrated in Figure 3, the dequantized coefficients are not equal to the original coefficients, but are close enough so that after the inverse transform is applied, the resulting image contains few or no visible artifacts.
In older video algorithms, such as MPEG-2, dequantization can require anywhere from about 3% up to about 15% of the processor cycles spent in a video decoding application. Cycles spent on dequantization in modern video algorithms (such as H.264) are negligible, as are the memory requirements.
Statistically Speaking
Next, the number of bits used to represent the quantized DCT coefficients is reduced by "coding," which takes advantage of some of the statistical properties of the coefficients. After quantization, many of the DCT coefficients—often, the vast majority of the high-frequency coefficients—are zero. A technique called "run-length coding" takes advantage of this fact by grouping consecutive zero-valued coefficients (a "run") and encoding the number of coefficients (the "length") instead of encoding the individual zero-valued coefficients.
Run-length coding is typically followed by variable-length coding (VLC). In variable-length coding, commonly occurring symbols (representing quantized DCT coefficients or runs of zero-valued quantized coefficients) are represented using code words that contain only a few bits, while less common symbols are represented with longer code words. By using fewer bits for the most common symbols, VLC reduces the average number of bits required to encode a symbol thereby reducing the number of bits required to encode the entire image.
On the decompression side, variable-length decoding (VLD) reverses the steps performed by the VLC block in the compression algorithm. Variable-length decoding is much more computationally demanding than variable-length coding. VLC performs one table lookup per symbol (where a symbol is encoded using multiple bits); in contrast, the most straightforward implementation of VLD requires a table lookup and some simple decision making to be applied for each bit. VLD requires an average of about 11 operations per input bit. Thus, the processing requirements of VLD are proportional to the video codec's selected bit rate. VLD can consume as much as 25% of the cycles spent in a video decoder implementation.
In a typical video decompression algorithm, the straightforward VLD implementation described above (which operates on one bit at a time) requires several kilobytes of lookup table memory. It is possible to improve the performance of the VLD by operating on multiple bits at a time, but this optimization requires the use of much larger lookup tables.
Some of the newer standards (such as H.264) replace or augment the run-length coding and VLC techniques described above to achieve greater compression. For example, H.264 supports both CAVLC (context-adaptive VLC) and CABAC (context-adaptive arithmetic coding). CAVLC augments VLC by adapting the coding scheme based on previously-coded coefficients. CABAC replaces VLC entirely, using instead a more efficient—but also more computationally demanding—scheme of arithmetic coding. CABAC can consume as many as 50% of the cycles in an H.264 decoder.
Looking at a bigger picture
All of the techniques described so far operate on each 8x8 block independently from any other block. Since images typically contain features that are much larger than an 8x8 block, more efficient compression can be achieved by taking into account the similarities between adjacent blocks in the image.
To take advantage of inter-block similarities, a prediction step is often added prior to quantization of the transform coefficients. In this step, codecs attempt to predict the image information within a block using the information from the surrounding blocks. Some codecs (such as MPEG-4) perform this step in the frequency domain, by predicting DCT coefficients. Other codecs (such as H.264) do this step in the spatial domain, and predict pixels directly. The latter approach is called "intra prediction."
In this step, the encoder attempts